Author: LocalHealthGuideEditor
Transgender regret? Research challenges narratives about gender-affirming surgeries
Harry Barbee, Johns Hopkins University; Bashar Hassan, Johns Hopkins University, and Fan Liang, Johns Hopkins University You’ll often hear lawmakers, activists and pundits argue that many transgender people regret their decision to have gender-affirming surgeries – a belief that’s been…
Psychedelics could make mental health worse in people with a personality disorder
Various personality disorders might respond differently to psychedelics. For instance, people with histrionic personality disorder (excessive attention-seeking and emotional overreaction) or borderline personality disorder (emotional instability, intense relationships and fear of abandonment) might feel worse or more unstable. And those with schizotypal personality disorder (social anxiety, odd beliefs and eccentric behaviour) could become more paranoid. People with narcissistic personality disorder (excessive self-importance, lack of empathy, and need for admiration) may struggle with the self-reflective nature of psychedelics because they often have a hard time handling criticism.
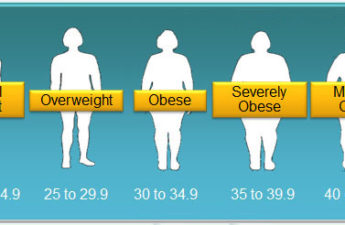
Stop asking me if I’ve tried keto: Why weight stigma is more than just being mean to fat people
Fat stigma can take the form of overt discrimination, but it is often insidious, pervasively entrenched into our society and environment.
Surgery won’t fix my chronic back pain, so what will?
Treatments offered to people with chronic pain include strong pain medicines such as opioids and invasive procedures such as spinal cord stimulators or spinal fusion surgery. Unfortunately, these treatments have little if any benefit and are associated with a risk of significant harm.
Nitazenes found in 5 overdose deaths in Philly – here’s what they are and why they’re so deadly
Researchers have relatively little information on how the human body reacts to nitazenes because the drugs have never gone through clinical trials. But lab tests show certain nitazenes could be hundreds to thousands of times more potent than morphine and 10 to 40 times stronger than fentanyl.
What is metabolism? A biochemist explains how different people convert energy differently − and why that matters for your health
Simply put, a primary role of metabolism is to convert chemical energy into electrical energy and back into chemical energy. How this energy is transferred throughout the body might play a central role in determining whether you’re sick or healthy.
Social media will tell you birth control causes mental health issues, weight gain and infertility – here are the facts
In recent years, there’s been a rise in misinformation about hormonal contraceptives on social media. Some women are reportedly even stopping their birth control as a result of misleading posts they’ve seen on TikTok and Instagram.
Drugs like Ozempic won’t ‘cure’ obesity but they might make us more fat-phobic
Ironically, while fat people are told they need to lose weight for their health, they are also shamed for “cheating” or taking shortcuts by using medication.
Increasingly sophisticated AI systems can perform empathy, but their use in mental health care raises ethical questions
Some examples of AI applications include: screening tools in primary care settings, enhanced tele-therapy sessions and chatbots offering accessible 24/7 emotional support. These can act as bridges for anyone waiting for professional help and those hesitant to seek traditional therapy. However, this turn to emotion-AI comes with a host of ethical, social and regulatory challenges around consent, transparency, liability and data security.
A natural deception: 3 marketing myths the supplement industry wants you to swallow
The business of supplements is booming, and with all the hype around them, it’s easy to forget what they actually are: substances that can powerfully affect the body and your health, yet aren’t regulated like drugs are.
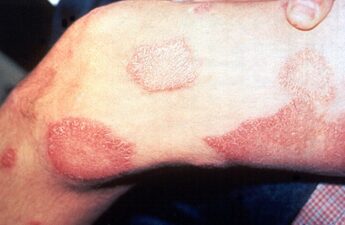
Leprosy cases are rising in the US – what is the ancient disease and why is it spreading now?
The word “leprosy” conjures images of biblical plagues, but the disease is still with us today.
Know Which Medication Is Right for Your Seasonal Allergies
An allergy is your body’s reaction to an otherwise innocent substance that it has identified as an invader. If you have allergies and encounter a trigger (allergen), your immune system fights it by releasing chemicals, such as histamine (hence the term “antihistamine”). Histamine causes symptoms, such as runny nose, itchy nose, sneezing, and itchy and watery eyes.
AI shown to dramatically speed protein engineering – UW study
Protein engineering scientists have been able to design more efficient proteins using machine learning quickly, dramatically shortening a process that typically takes months to years of trial and error.
Considering taking a weight-loss drug like Ozempic? Here are some potential risks and benefits
As they’ve grown in popularity, we’ve also heard more about the potential side effects – from common gastrointestinal discomforts, to more serious mental health concerns.
Hospice care for those with dementia falls far short of meeting people’s needs at the end of life
Strikingly, only 12% of Americans with dementia ever enroll in hospice. Among those who do, one-third are near death. This is in stark contrast to the cancer population: Patients over 60 with cancer enroll in hospice 70% of the time. In my experience caring for dementia patients, the underuse of hospice by dementia patients has more to do with how hospice is structured and paid for in the U.S. than it does patient preference or differences between cancer and dementia.