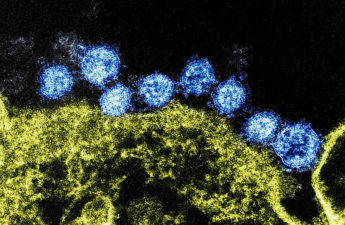
Bird Flu Cases Rise to 31, But CDC Says No Person-To-Person Transmission
The number of people infected with bird flu in the U.S. has risen to at least 31, federal health officials said Thursday, but there is no evidence of human-to-human spread after blood tests confirmed health workers in Missouri caring for a hospitalized patient were not infected. Speaking to reporters during a briefing, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) officials said multiple tests confirmed five symptomatic health workers did not have any evidence of infection. TheHill.
How to Spot Early Signs of Potentially Fatal Whooping Cough as Cases Rise
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has reported 18,506 cases of whooping cough between January 1 and October 12—five times more than the same time frame in 2023, according to preliminary data. Cases are not evenly spread throughout the U.S. The Minnesota Department of Health announced on October 10 that the state had seen 1,019 cases so far in 2024, including 376 cases in Hennepin County and more than 40 cases in each of its surrounding counties. Newsweek.
Onions From California-Based Produce Company Linked to E. Coli Outbreak, McDonald’s Says
A California-based produce company was the source of fresh onions linked to a deadly E. coli food poisoning outbreak at McDonald’s, officials with the restaurant chain said Thursday. Meanwhile, other fast-food restaurants — including Taco Bell, Pizza Hut, KFC and Burger King — pulled onions from some menus. McDonald’s officials said that Taylor Farms, of Salinas, California, sent onions to one distribution facility, which led the fast-food chain to remove Quarter Pounder hamburgers from restaurants in several states. McDonald’s didn’t say which facility it was. AP.
US Government Shares New Pandemic Plan
U.S. government officials, together with counterparts in Canada and Mexico, have unveiled their latest plans to strengthen regional health security and pandemic preparedness. … The collaboration, called the North American Preparedness for Animal and Human Pandemics Initiative, or NAPAHPI, has been described as a “flexible, scalable, cross-sectoral” platform which aims to strengthen regional capacities for disease control, built on lessons learned from COVID-19 and other healthy security events. Newsweek.
One in 14 American Patients May Be Harmed by Hospital Diagnosis Mistakes
Harmful diagnostic errors may occur for as many as one in every 14 hospital patients receiving medical care, a new study based on a single medical center in the U.S. has found. As many as 85 percent of these errors may be preventable, highlighting the need for improved surveillance in hospital settings. … In their study, published in the journal BMJ Quality and Safety, [Anuj Dalal, an associate professor at Harvard Medical School and lead author on the study] and colleagues concluded that, based on this sample from a single medical center, harmful diagnostic errors occurred in 7 percent of patients, or one in 14, receiving general medical care. They added that the majority of these errors were preventable. Newsweek.
AHA, FBI Partner to Mitigate Healthcare Targeted Violence: 4 Things to Know
The American Hospital Association and the FBI’s Behavioral Analysis Unit have collaborated to create resources to mitigate targeted violence in healthcare settings, including threat assessment and prevention strategies. Healthcare industry workers experience the highest rate of injury from workplace violence and are five times as likely to suffer a workplace violence injury compared to workers overall, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Beckers.
EPA Imposes Stricter Standards to Protect Children from Exposure to Lead Paint
Two weeks after setting a nationwide deadline for removal of lead pipes, the Biden administration is imposing strict new limits on dust from lead-based paint in older homes and child-care facilities. A final rule announced Thursday by the Environmental Protection Agency sets limits on lead dust on floors and windowsills in pre-1978 residences and child-care facilities to levels so low they cannot be detected. AP.
GAO Report Shows How US Schools Spent Pandemic Relief Funds, Including On Better Ventilation
A new report from the US Government Accountability Office (GAO) concludes that, by the end of the 2021-22 school year, US school districts had spent about $60 billion in federal COVID-19 emergency aid through the Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) fund. Eighty percent of this money was used to address students’ social-emotional needs and to keep schools running, while 20% went to addressing health concerns, including improving ventilation, enhanced cleaning and disinfection, and hiring school psychologists. CIDRAP.