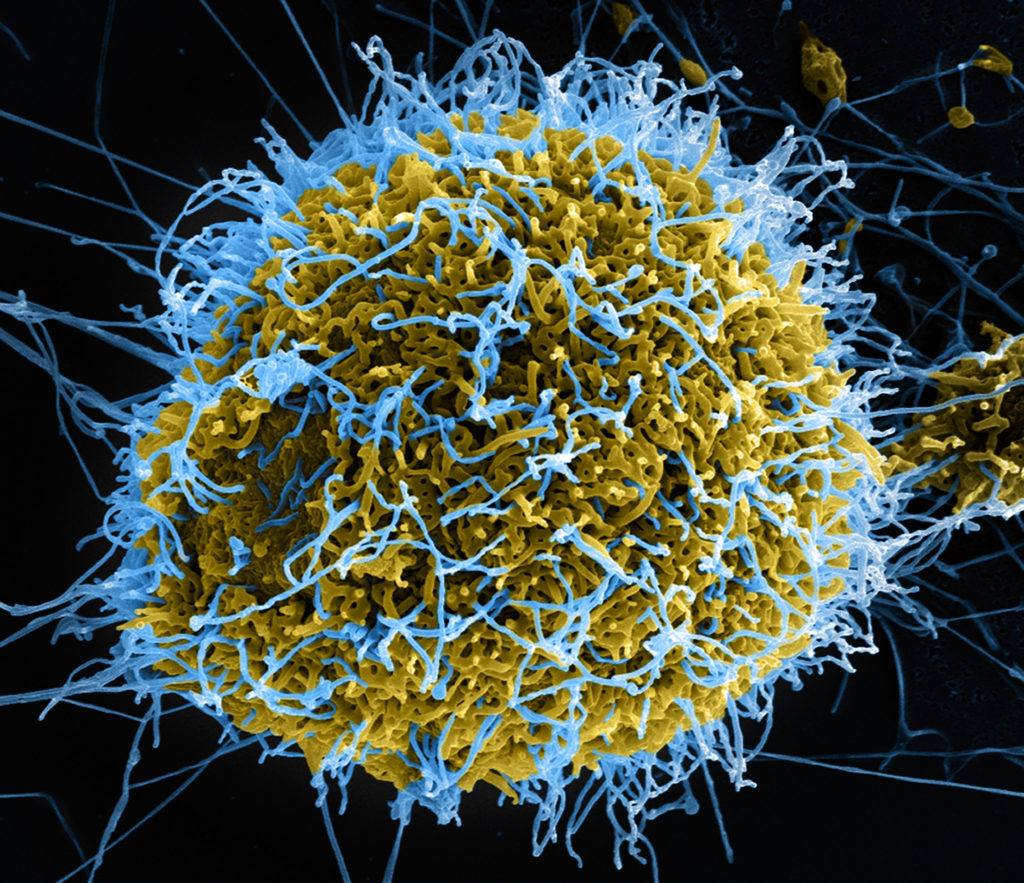
Colorized scanning electron micrograph of filamentous Ebola virus particles (blue) budding from a chronically infected cell. Credit: NIAID
Why so many epidemics originate in Asia and Africa – and why we can expect more
Suresh V Kuchipudi, Pennsylvania State University
The coronavirus disease, known as COVID-19, is a frightening reminder of the imminent global threat posed by emerging infectious diseases.
Although epidemics have arisen during all of human history, they now seem to be on the rise.
In just the past 20 years, coronaviruses alone have caused three major outbreaks worldwide. Even more troubling, the duration between these three pandemics has gotten shorter.
I am a virologist and associate director of the Animal Diagnostic Laboratory at Penn State University, and my laboratory studies zoonotic viruses, those that jump from animals and infect people.
Most of the pandemics have at least one thing in common: They began their deadly work in Asia or Africa. The reasons why may surprise you.
Population explosion and changing urban landscapes
An unprecedented shift in human population is one reason why more diseases originate in Asia and Africa. Rapid urbanization is happening throughout Asia and the Pacific regions, where 60% of the world already lives. According to the World Bank, almost 200 million people moved to urban areas in East Asia during the first decade of the 21st century. To put that into perspective, 200 million people could form the eighth most populous country in the world.
Migration on that scale means forest land is destroyed to create residential areas. Wild animals, forced to move closer to cities and towns, inevitably encounter domestic animals and the human population. Wild animals often harbor viruses; bats, for instance, can carry hundreds of them. And viruses, jumping species to species, can ultimately infect people.
Eventually, extreme urbanization becomes a vicious cycle: More people bring more deforestation, and human expansion and the loss of habitat ultimately kills off predators, including those that feed off rodents. With the predators gone – or at least with their numbers sharply diminished – the rodent population explodes. And as studies in Africa show, so does the risk of zoonotic disease.
The situation is only likely to get worse. A major proportion of East Asia’s population still lives in rural areas. Urbanization is expected to continue for decades.
Subsistence agriculture and animal markets
Tropical regions, rich in host biodiversity, already hold a large pool of pathogens, greatly increasing the chance that a novel pathogen will emerge. The farming system throughout Africa and Asia doesn’t help.
On both continents, many families depend on subsistence farming and a minuscule supply of livestock. Disease control, feed supplementation and housing for those animals is extremely limited. Cattle, chickens and pigs, which can carry endemic disease, are often in close contact with each other, a variety of nondomestic animals and humans.
And not just on the farms: Live animal markets, commonplace throughout Asia and Africa, feature crowded conditions and the intimate mixing of multiple species, including humans. This too plays a key role in how a killer pathogen could emerge and spread between species.
Another risk: bushmeat hunting and butchering, which is particularly widespread in sub-Saharan Africa. These activities, as they threaten animal species and irrevocably change ecosystems, also bring people and wild animals together. Bushmeat hunting is a clear and primary path for zoonotic disease transmission.
So is traditional Chinese medicine, which purports to provide remedies for a host of conditions like arthritis, epilepsy and erectile dysfunction. Although no scientific evidence exists to support most of the claims, Asia is an enormous consumer of traditional Chinese medicine products.
Tigers, bears, rhinos, pangolins and other animal species are poached so their body parts can be mixed into these questionable medications. This, too, is a major contributor to increasing animal-human interactions. What’s more, demand is likely to go up, as online marketing soars along with Asia’s relentless economic growth.
A matter of time
The viruses, thousands of them, continue to evolve. It’s just a matter of time before another major outbreak occurs in this region of the world. All the coronaviruses that caused recent epidemics, including the COVID-19, jumped from bats to another animal before infecting humans.
It’s difficult to predict precisely what chain of events cause a pandemic, but one thing is certain: these risks can be mitigated by developing strategies to minimize human effects which contribute to the ecological disturbances.
As the current outbreak has shown, an infectious disease that starts in one part of the world can spread globally in virtually no time whatsoever. There is an urgent need for constructive conservation strategies to prevent deforestation and reduce animal-human interactions. And a comprehensive global surveillance system to monitor the emergence of these diseases – now missing – would be an indispensable tool in helping us fight these deadly and terrifying epidemics.
[Deep knowledge, daily. Sign up for The Conversation’s newsletter.]
Suresh V Kuchipudi, Clinical Professor and Associate Director of Animal Diagnostic Laboratory, Pennsylvania State University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.