Category: Infectious Disease
How the Paris Olympics could become a super-spreader event for dengue
Visitors from more than 200 countries are expected in France for the Olympics. Many of those countries are already experiencing dengue this year.
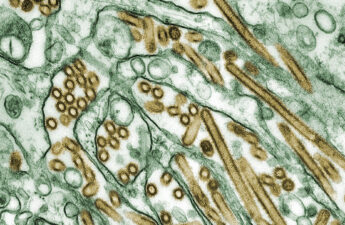
Fragments of bird flu genetic material (RNA) were found in cow’s milk from the dairy herds associated with infected US farmers.
Masks work, our comprehensive review has found
The more people wore their masks, the more effective the masks turned out to be.
High H5N1 influenza levels found in mice given raw milk from infected dairy cows
The results suggest that consumption of raw milk by animals poses a risk for H5N1 infection and raises questions about its potential risk in humans.
Future pandemics will have the same human causes as ancient outbreaks
Lessons from anthropology can help prevent them
Studies test possible treatments for long COVID
NIH to open long COVID clinical trials to study sleep disturbances, exercise intolerance, and post exertional malaise
CDC warns of E. coli outbreak linked to organic walnuts sold in bulk
Almost all sick people purchased organic walnuts from bulk bins in food co-ops or natural food stores in California and Washington.
Need a rapid health test? Try our kiosks.
Washington State Department of Health (DOH)-sponsored kiosks with free COVID-19 tests, flu tests, and more are popping up all over Washington. Let’s dig into the what, where, and why.
How bird flu virus fragments get into milk sold in stores, and what the spread of H5N1 in cows means for the dairy industry and milk drinkers
The discovery of fragments of avian flu virus in milk sold in U.S. stores, including in about 20% of samples in initial testing across the country, suggests that the H5N1 virus may be more widespread in dairy cattle than previously realized.
Fecal pollution threatens popular shellfish harvest areas
Fifteen of Washington’s 115 commercial shellfish growing areas may face harvest restrictions because of increased fecal bacteria levels in the water.
Infections after surgery are more likely due to bacteria already on your skin than from microbes in the hospital − UW researchers find
Research comparing bacteria in the microbiome – those colonizing our noses, skin and other areas of the body – with the bacteria that cause pneumonia, diarrhea, bloodstream infections and surgical site infections shows that the bacteria living innocuously on our own bodies when we’re healthy are most often responsible for these bad infections when we’re sick.
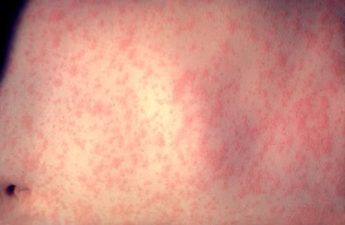
PUBLIC HEALTH MONITORING MEASLES EXPOSURE AMONG INTERNATIONAL TRAVELERS VISITING SEATTLE
Last week that a group of international travelers visiting Seattle were exposed to an individual with measles prior to arriving in Seattle. Currently, there are no cases of measles among the group (or within King County), but Public Health — Seattle & King County is monitoring the situation closely.
Drugs like Ozempic won’t ‘cure’ obesity but they might make us more fat-phobic
Ironically, while fat people are told they need to lose weight for their health, they are also shamed for “cheating” or taking shortcuts by using medication.
Leprosy cases are rising in the US – what is the ancient disease and why is it spreading now?
The word “leprosy” conjures images of biblical plagues, but the disease is still with us today.
Cardiovascular risks and COVID-19: New research confirms the benefits of vaccination
A new study found that common cardiovascular complications of COVID-19 were substantially reduced in people who were vaccinated, with protective effects lasting up to a year after vaccination.