Category: Social Determinants of Health
The number of births continues to fall, despite abortion bans
Births continued a historic slide in all but two states last year, making it clear that a brief post-pandemic uptick in the nation’s birth numbers was all about planned pregnancies that had been delayed temporarily by COVID-19.
Future pandemics will have the same human causes as ancient outbreaks
Lessons from anthropology can help prevent them
The Lasting Impact of Exposure to Gun Violence
Since 2020, gun violence has overtaken motor vehicle crashes to become the leading cause of death for children and adolescents aged 1 to 19 in the United States — a change mainly driven by homicides.
US birth rates are at record lows – even though the number of kids most Americans say they want has held steady
Birth rates are falling in the U.S. Is this decline because, as some suggest, young people aren’t interested in having children? Or are people facing increasing barriers to becoming parents?
Older adults want to ‘age in place,’ but their options are limited in most states
As America gets grayer, advocates are pushing for new types of housing. By Robbie Sequiera, Staff ReporterStateline As older adults begin to outnumber young people in the United States in the coming decade, advocacy groups are challenging states to shift…
Federal shutdown should not immediately threaten food aid for WA mothers and kids
WIC provides food assistance to mothers and children up to 5 years old. In July, about 130,400 people received benefits from the program in Washington, including around 25,600 infants and 76,400 kids older than 1 year.
Study Reveals Staggering Toll of Being Black in America: 1.6M Excess Deaths Over 22 Years
Because so many Black people die young — with many years of life ahead of them — their higher mortality rate from 1999 to 2020 resulted in a cumulative loss of more than 80 million years of life compared with the white population, the study showed.
Most Americans Say They or a Family Member Has Experienced Gun Violence
Nearly 1 in 5 respondents , including 34% of Black adults, 18% of Hispanic adults, and 17% of white adults, said a family member had been killed by a gun.
Why Finland is the happiest country in the world – an expert explains
Finland comes out top, followed by Denmark and Iceland. Just why Finns are happier than others comes down to a number of factors including lower income inequality (most importantly, the difference between the highest paid and the lowest paid), high social support, freedom to make decisions, and low levels of corruption.
Being ‘Socially Frail’ Comes With Health Risks for Older Adults
Social frailty is a corollary to physical frailty, a set of vulnerabilities (including weakness, exhaustion, unintentional weight loss, slowness, and low physical activity) shown to increase the risk of falls, disability, hospitalization, poor surgical outcomes, admission to a nursing home, and earlier death in older adults.Essentially, people who are physically frail have less physiological strength and a reduced biological ability to bounce back from illness or injury.
Mental Health Care Must Promote Wellness, Not Just Treat Illness
The nation’s mental health care system is currently focused almost exclusively on preventing and treating mental illness — conditions like depression, anxiety, and personality disorder that adversely affect a person’s mood and behavior. Although these are critical factors in mental health, so too are the components of life that are associated with feeling good, finding happiness and meaning, connecting with others, and feeling engaged — qualities that can be collectively described as positive mental health, or mental wellness.
Epigenetic and social factors both predict aging and health – but new research suggests one might be stronger
For years, researchers have been using clinical factors normally collected at physicals, like hypertension, cholesterol and weight, as indicators to predict aging. The idea was that these measures could determine whether someone is a fast or slow ager at any point in their life cycle. But more recently, researchers have theorized that there are other biological markers that reflect aging at the molecular and cellular level. This includes modifications to a person’s genetic material itself, or epigenetics.
A journey from work to home is about more than just getting there – the psychological benefits of commuting that remote work doesn’t provide
During the shift to remote work, many people lost this built-in support for these important daily processes. Without the ability to mentally shift gears, people experience role blurring, which can lead to stress. Without mentally disengaging from work, people can experience burnout.
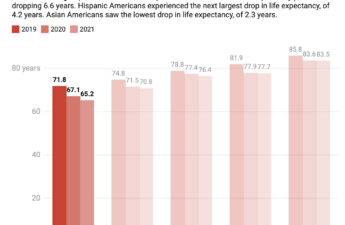
Native Americans have experienced a dramatic decline in life expectancy during the COVID-19 pandemic – but the drop has been in the making for generations
Even before COVID-19 emerged, life expectancy for Indigenous men was already five years lower than for non-Hispanic white men in the United States.
Marriage provides health benefits – and here’s why
One theory that seeks to explain the link between marriage and health is the act of self-selection. Simply put, people who are wealthier and healthier than average are more likely not only to get married but also to find a partner who is wealthier and healthier than average. While this may be part of the story, marriage also provides partners with a sense of belonging, more opportunities for social engagement and reduced feelings of loneliness. This social integration, or the extent to which people participate in social relationships and activities, can greatly influence health – from reducing the risk of hypertension and heart disease to lowering one’s risk of death or suicide.