Category: Painkillers
Medetomidine is replacing xylazine in Philly street fentanyl − creating new hurdles for health care providers and drug users
Kory London, Thomas Jefferson University and Karen Alexander, Thomas Jefferson University Philadelphia’s street opioid supply – or “dope” market – is constantly changing. As health care workers and researchers who care for people who use drugs in our community, we…
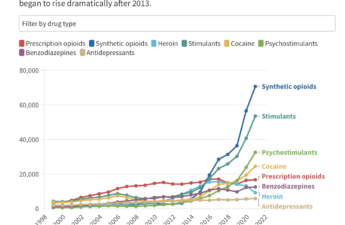
Stimulant Users Are Caught in Fatal ‘Fourth Wave’ of Opioid Epidemic
The first wave of the long-running and devastating opioid epidemic began in the United States with the abuse of prescription painkillers in the early 2000s. The second wave involved an increase in heroin use, starting around 2010. The third wave began when powerful synthetic opioids such as fentanyl started appearing in the supply around 2015. Now experts are observing a fourth phase of the deadly epidemic.
Fentanyl 101
As little as 2 mg of fentanyl (which can fit on the tip of a pencil) can be enough to kill the average American. People can also unknowingly consume fentanyl when it is mixed into or sold as other drugs, including heroin, cocaine, or counterfeit pills.
The Incidental Economist Takes an In-Depth Look at America’s Opioid Crisis
This compilation is a deep dive on the opioid crisis, thanks in part to funding by the NIHCM. Explore the history of opioids, the science of opioids, and learn about how and why attitudes and US policy regarding addiction treatment and opioid control need to change.
More than 321,000 U.S. children lost a parent to drug overdose from 2011 to 2021
The highest number of affected children were those with non-Hispanic white parents, but communities of color and tribal communities were disproportionately affected.
Need a rapid health test? Try our kiosks.
Washington State Department of Health (DOH)-sponsored kiosks with free COVID-19 tests, flu tests, and more are popping up all over Washington. Let’s dig into the what, where, and why.
Surgery won’t fix my chronic back pain, so what will?
Treatments offered to people with chronic pain include strong pain medicines such as opioids and invasive procedures such as spinal cord stimulators or spinal fusion surgery. Unfortunately, these treatments have little if any benefit and are associated with a risk of significant harm.
Nitazenes found in 5 overdose deaths in Philly – here’s what they are and why they’re so deadly
Researchers have relatively little information on how the human body reacts to nitazenes because the drugs have never gone through clinical trials. But lab tests show certain nitazenes could be hundreds to thousands of times more potent than morphine and 10 to 40 times stronger than fentanyl.
King County launches ‘bup’ hotline.
Buprenorphine, also called suboxone, is a medication used to treat opioid use disorder. It is one of the best available treatments to alleviate withdrawal, reduce cravings, and reduce overdose risk by about half when taken as directed. It works by binding to the same receptors that opioids like fentanyl bind to, but it only turns them on about halfway. That keeps people from feeling sick and helps with their cravings.
Oregon’s Drug Decriminalization Aimed to Make Cops a Gateway to Rehab, Not Jail. State Leaders Failed to Make It Work.
Ballot Measure 110, approved by voters in 2020, created a new role for law enforcement in Oregon. While there’s evidence people living with addiction in the state are increasingly finding their way into treatment, the failure to turn police encounters into successful on-ramps to rehab has been cited by critics as prime evidence the measure isn’t working. Oregon lawmakers, noting an ongoing rise in overdose deaths, are now looking to restore jail time for drug possession.
But Oregon’s political leaders themselves played central roles in failing to deliver on the potential for law enforcement to connect people with lifesaving services under the new measure, documents and interviews with a wide array of people involved in the system indicate.
Most people with chronic back pain naturally think their pain is caused by injuries or other problems in the body such as arthritis or bulging disks. But our research team has found that thinking about the root cause of pain as a process that’s occurring in the brain can help promote recovery.
The roots of the North American opioid crisis, and 3 key strategies for stopping it
The traditional “war on drugs” approach that focuses only on criminalization has been unsuccessful. In reality the data shows that illegal drug prices have fallen whilst purity and deaths have increased. Overdose deaths have also increased in prisons showing that places with even the highest level of security are vulnerable to drug smuggling.Focusing on the opioid crisis through a public-health approach includes massively increasing access to care and treatment for patients experiencing substance use disorder. It requires more evidence-based services such as addiction clinics, psychotherapy harm reduction strategies and education for both patients and families about treatments that are available to them.Beyond initial treatment there should be continued professional social support and a wider national effort to address the socioeconomic causes in disadvantaged communities.
States stiffen penalties for fentanyl, despite public health concerns
Critics argue that harsh penalties could deter those in need of help and worsen societal disparities.
Acetaminophen vs ibuprofen — which works best and when?
Deciding which one you should choose is dependent on the type of pain you are experiencing. Sometimes it might be appropriate to take a medication that contains both drugs.
Addiction Treatment May Be Coming to a Pharmacy Near You
new study showed patients who receive the medicine at pharmacies rather than at doctor’s offices stayed in treatment longer.