Category: Cardiology
AI inconsistently assesses cardiac risk from chest pain – UW study finds
Tasked to interpret data associated with patient complaints of nontraumatic chest pain, the ChatGPT-4 large language model performed poorly against two standard tools that doctors use to predict risk of a cardiac event.
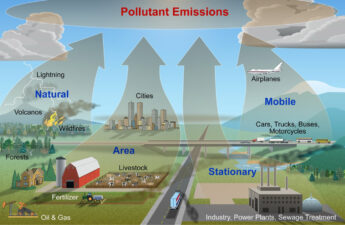
What are the health costs of air pollution, and what can we do about it?
Have you ever noticed the hazy smog that hangs over cities or the lingering smell of exhaust fumes from traffic? These are just a few noticeable signs of air pollution, a threat that can have a significant effect on our health and well-being.
Your heart changes in size and shape with exercise – this can lead to heart problems for some athletes and gym rats
Exercise can significantly reduce the risk of developing conditions that affect the heart, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol and obesity. But large amounts of exercise throughout life may also harm the heart, leading to the development of a condition called athletic heart.
It’s time for a heart-to-heart about women’s cardiovascular health, unique risk factors and symptoms
Although cardiovascular disease is often considered a disease of men, women are more likely to die from a heart attack when compared with men. This fact often surprises women and even their health-care providers. Many women are not aware that heart disease is a significant health threat to them, but the reality is that five times as many women die from heart disease as breast cancer.
This salt alternative could help reduce blood pressure. So why are so few people using it?
It’s hard for people to change the way they cook, season their food differently, pick low-salt foods off the supermarket shelves and accept a less salty taste.
Now there is a simple and effective solution: potassium-enriched salt. It can be used just like regular salt and most people don’t notice any important difference in taste.
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in King County spiked during pandemic, UW study finds
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrests rose by 19% and survival of those events fell by about 4% during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic. But acute infections of the SARS-CoV-2 virus appeared not to be a primary cause of the changes.
What is atrial fibrillation, the heart condition US President Joe Biden lives with?
More than 37.5 million people globally also have atrial fibrillation, but many don’t realise they have it. For most, the condition has few symptoms and does not limit daily life. However, identifying it and treating it is the only way to reduce its serious health consequences.
Acetaminophen vs ibuprofen — which works best and when?
Deciding which one you should choose is dependent on the type of pain you are experiencing. Sometimes it might be appropriate to take a medication that contains both drugs.
In the “Wild West” of Outpatient Vascular Care, Doctors Can Reap Huge Payments as Patients Risk Life and Limb
To move vascular procedures out of expensive hospitals, the government turbocharged payments to doctors’ offices. Instead of saving money, it started a boom that is making doctors rich and putting patients in danger.
Risk of rehospitalization in younger women after heart attack nearly double that of men
Higher rates of risk factors such as obesity, heart failure, and depression among women most likely contributed to the disparity.
Many Americans wrongly assume they understand what normal blood pressure is – and that false confidence can be deadly
Nearly half of Americans ages 20 years and up – or more than 122 million people – have high blood pressure. And even if your numbers are normal right now, they are likely to increase as you age; more than three-quarters of Americans age 65 and older have high blood pressure.
Damar Hamlin’s cardiac arrest shows need for CPR training and emergency defibrillators in public spaces
Adam Pyle, University of Toronto Football — a sport that involves violent collisions — came under shocking scrutiny on Jan. 2 when Buffalo Bills player Damar Hamlin collapsed from a cardiac event immediately following an on-field collision. Most fans already…
What caused Damar Hamlin’s heart to stop?
Damar Hamlin’s cardiac arrest during ‘Monday Night Football’ could be commotio cordis or a more common condition – a heart doctor answers 4 questions
Study challenges “good” cholesterol’s role in universally predicting heart disease risk
Lower levels of HDL cholesterol were associated with increased risks for heart attacks in white but not Black adults, and higher levels were not protective for either group. the study was the first to find that lower HDL cholesterol levels only predicted increased cardiovascular disease risk for white adults.
Heartbeat-Tracking Technology Raises Patients’ and Doctors’ Worries
Gadget firms — starting with Apple and now Fitbit, which is owned by Google — are selling wearable devices that check heartbeat rhythms and alert users when something is out of sync. But some cardiologists say the information the devices produce isn’t always useful.