Category: Infectious Disease
NY polio case linked to overseas virus
Rockland County, a suburban area northwest of New York City, sought medical treatment in June for weakness and paralysis. He had not been vaccinated against polio.
Monkeypox Straining Already Overstretched Public Health System
Echoing the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, demand for monkeypox vaccine doses far outstrips supply, appointments have been difficult to get, and money and personnel have had to shift from other priorities.
How Polio Crept Back Into the U.S.
U.S. public health agencies generally don’t test wastewater for signs of polio. That may have given the virus time to circulate silently before it paralyzed a New York man.
How effective are face masks?
In one study, those who always wore any type of mask or respirator in indoor public spaces were 56% less likely to test positive than those that never wore one. There was an 83% reduction in the odds of getting a positive test in those who wore a respirator, compared with a 66% reduction in those wearing surgical masks. Those wearing a cloth mask had lower odds of having a positive PCR test result than those wearing no mask, but the difference was not statistically significant.
Video: Why the public health system is struggling to contain monkeypox
Funding cuts and outdated technology are hampering the U.S. response on the ground as monkeypox cases continue to rise.
Boost Now or Wait? Many Wonder How Best to Ride Out Covid’s Next Wave
Consistent messaging has been complicated by the different views of leading vaccine scientists. Although physicians like del Rio and Dr. Peter Hotez of Baylor College of Medicine see the value in getting a second booster, Dr. Paul Offit, a member of the FDA’s vaccine advisory committee, is skeptical it’s needed by anyone but seniors and people who are immunocompromised.
Monkeypox FAQ:
How is it transmitted? Where did it come from? What are the symptoms? Does smallpox vaccine prevent it?
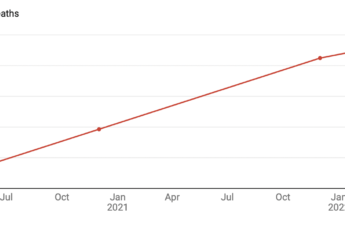
1 in 8 U.S. deaths from 2020 to 2021 came from COVID-19 – leaving millions of relatives reeling from distinctly difficult grief
More than 9 million Americans have lost a close relative to COVID-19, a dramatic rise in bereavement that makes them vulnerable to mental distress.
Should you get a COVID-19 booster shot now or wait until fall? Two immunologists help weigh the options
Clinical studies show that mixing and matching booster vaccines can lead to a more robust immune response.
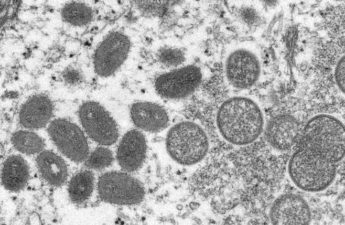
What You Need to Know About Monkeypox
Monkeypox is a viral infection, a close cousin of smallpox. But it causes a much milder disease. It is transmitted through close contact, including sex, kissing, and massage — any kind of contact of the penis, vagina, anus, mouth, throat, or even skin. In the current outbreak, monkeypox has primarily been transmitted sexually.
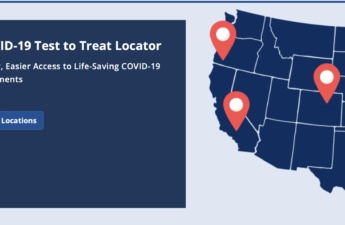
Fast Access to COVID-19 Treatment in Washington
Test to Treat is a national program that gives people a fast way to access free lifesaving treatment for COVID-19. Through this program, people are able to get tested and — if they are positive and treatments are appropriate for them — receive a prescription from a health care provider, and have their prescription filled all at one location. Think of it as a one-stop-shop for treating COVID-19.
Will the US Overcome Its Covid Complacency Even as the Threat Returns?
Two years ago, pre-vaccine, the images of dying people on ventilators saying goodbye on iPads, doctors in hazmat suits, and portable morgues in hospital parking lots briefly engaged everyone in the need for public health resources, and Congress stepped up. Now, the public has moved on. But the threat hasn’t gone away. And there will be a price to pay.
The latest on COVID-19 boosters
Boosters are important for keeping our communities safe, especially as COVID-19 cases increase across Washington. But it’s not always easy to track when you or a loved one is eligible for a first, or a second, booster. Here’s what you need to know.
WHEN CAN BABIES AND YOUNG CHILDREN FINALLY GET THE COVID VACCINE?
Public Health – Seattle & King County wants to ensure that families across the county can protect their children under 5 with COVID-19 vaccine soon after authorization for emergency use occurs.
Herd immunity was sold as the path out of the pandemic. Here’s why we’re not talking about it any more
As the pandemic progressed, herd immunity via vaccination moved further and further out of reach. In fact, based on what we know about currently circulating viral variants, today, herd immunity via vaccination is mathematically impossible.