Category: Coronavirus
Health News Headlines
Abortion rates rises – Lead in schools – Vision and hearing loss linked to dementia
COVID infections spreading in Oregon, Washington and California
Washington saw 2,905 positive COVID tests in the week ending July 27. The weekly trend rate, which is determined by taking the number of positive tests divided by the population and multiplying by 100,000, is 36.9. The weekly rate of positive tests has gone up steadily over recent weeks. The average number of hospitalizations over the week ending in July 27 was 260. Just over 3% of hospital beds in the state were occupied by COVID patients.
COVID-19 deaths are declining, but some people face greater risk
In the more than four years since COVID-19 emerged, COVID-19 deaths have declined overall, but the disease remains dangerous to many. Anyone who contracts COVID-19 is at risk of severe illness, death, heart problems, and long COVID.
Looking for Long Covid: A Clash of Definition and Study Design
Few experts dispute that long Covid can be debilitating, or that it warrants careful study. But in interviews with Undark, a number of experts said that it is misleading to frame long Covid as an increasing threat. The best data, they say, suggest that most people recover from the disorder and that long Covid rates will decline as people develop immunity.
Studies test possible treatments for long COVID
NIH to open long COVID clinical trials to study sleep disturbances, exercise intolerance, and post exertional malaise
Need a rapid health test? Try our kiosks.
Washington State Department of Health (DOH)-sponsored kiosks with free COVID-19 tests, flu tests, and more are popping up all over Washington. Let’s dig into the what, where, and why.
Cardiovascular risks and COVID-19: New research confirms the benefits of vaccination
A new study found that common cardiovascular complications of COVID-19 were substantially reduced in people who were vaccinated, with protective effects lasting up to a year after vaccination.
ASK PUBLIC HEALTH: WHAT ARE THE LATEST RECOMMENDATIONS FOR STAYING AT HOME WHEN SICK?
We sat down with Dr. Eric Chow, Chief of Communicable Disease at Public Health – Seattle & King County to get the latest update and hear what our community can do to continue to prevent illness and what parents, schools, and our community should know.
Washington streamlines guidance for COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses
The Washington State Department of Health announced updated guidance for what to do when someone is sick with COVID-19, flu, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and other respiratory viruses.
Fall Covid-19 Update
Will there be a new surge?
Who should get the new mRNA vaccines?
Are they safe and effective?
CDC Recommends Updated COVID-19 Vaccine for Fall/Winter Virus Season
Vaccination remains the best protection against COVID-19-related hospitalization and death. Vaccination also reduces your chance of suffering the effects of Long COVID, which can develop during or following acute infection and last for an extended duration. If you have not received a COVID-19 vaccine in the past 2 months, get an updated COVID-19 vaccine to protect yourself this fall and winter.
COVID-19 vaccine boosters are the best defence: Older adults shouldn’t rely on previous infection for immunity
We found that those who had battled the BA.1-2 variant of Omicron in early 2022 had a 30-fold higher risk of contracting the BA.5 variant later in the year. That was exactly the opposite of what we, or anyone, would have predicted. What the findings do tell us is that older adults who have had a previous COVID-19 infection shouldn’t rely on that to protect them against reinfection this fall. To protect against severe illness, keeping booster shots up to date is recommended.
Activist Misuses Federal Data to Make False Claim That Covid Vaccines Killed 676,000
There is no evidence that covid vaccines have killed Americans in large numbers, let alone 676,000. We rate the claim Pants on Fire!
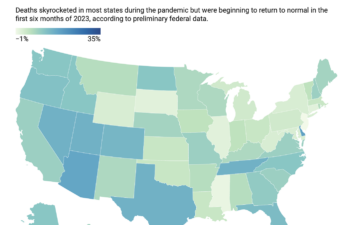
Death counts remain high in some states even as COVID fatalities wane
Fatalities from other causes such as traffic accidents, murders and overdoses are still on the rise.
COVID-19 vaccination and boosting during pregnancy benefits pregnant people and newborns
The researchers found that pregnant women who received the COVID-19 vaccines generated antibodies against specific types of SARS-CoV-2. These antibodies crossed the placenta and were also found in the cord blood of vaccinated participants. This likely conferred some protection in the newborns against infection immediately after birth—a critical time when they are vulnerable to severe COVID-19 disease but are too young to be vaccinated.