Category: Influenza/Flu
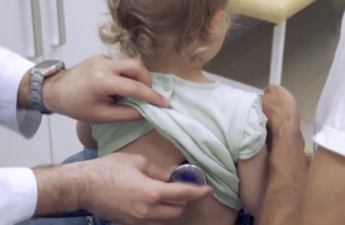
Bird Flu Cases Are Going Undetected, New Study Suggests. It’s a Problem for All of Us.
s bird flu cases go underreported, health officials risk being slow to notice if the virus were to become more contagious. A large surge of infections outside of farmworker communities would trigger the government’s flu surveillance system, but by then it might be too late to contain.
Fragments of bird flu genetic material (RNA) were found in cow’s milk from the dairy herds associated with infected US farmers.
Masks work, our comprehensive review has found
The more people wore their masks, the more effective the masks turned out to be.
High H5N1 influenza levels found in mice given raw milk from infected dairy cows
The results suggest that consumption of raw milk by animals poses a risk for H5N1 infection and raises questions about its potential risk in humans.
How bird flu virus fragments get into milk sold in stores, and what the spread of H5N1 in cows means for the dairy industry and milk drinkers
The discovery of fragments of avian flu virus in milk sold in U.S. stores, including in about 20% of samples in initial testing across the country, suggests that the H5N1 virus may be more widespread in dairy cattle than previously realized.
Washington streamlines guidance for COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses
The Washington State Department of Health announced updated guidance for what to do when someone is sick with COVID-19, flu, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and other respiratory viruses.
As bird flu continues to spread in the US and worldwide, what’s the risk that it could start a human pandemic? 4 questions answered
An outbreak of H5N1 avian influenza that started in 2021 has become the largest bird flu outbreak in history, both in the U.S. and worldwide. In the U.S. the virus has led to the destruction of millions of commercially raised chickens, turkeys, ducks and geese, and has killed thousands of wild birds. Many virologists are concerned that this virus could spill over to humans and cause a new human pandemic.
How do you make a universal flu vaccine?
University of Washington School of Medicine microbiologist Deborah Fuller explains the challenges, and how mRNA could offer a promising solution
As viral infections skyrocket, masks are still a tried-and-true way to help keep yourself and others safe
Wearing a surgical mask in an indoor public setting reduces the odds of testing positive for COVID-19 by 66%, and wearing an N95/KN95 type of mask lowers the odds of testing positive by 83%.
King County reports first child flu death of the 2022-2023 flu season
This death comes on top of a steep and unprecedented rise in illnesses and hospitalizations in King County and nationally among children for infections caused by multiple respiratory viruses.
COVID-19, RSV and the flu are straining health care systems – two epidemiologists explain what the ‘triple threat’ means for children
The underlying reasons for the convergence of these viruses and the increase in infections so early in the season are not yet clear. But health experts have some clues about contributing factors and what it could mean for the coming months.
COVID, flu, RSV – how this triple threat of respiratory viruses could collide this winter
As the days get shorter and the weather colder in the northern hemisphere, health officials have warned of a perfect storm of infectious respiratory diseases over the winter months.
Why taking fever-reducing meds and drinking fluids may not be the best way to treat flu and fever
As flu season progresses, so does the chorus of advice, professional and otherwise, to drink plenty of fluids and take fever-reducing medications, like acetaminophen, ibuprofen or aspirin. These recommendations, well-intentioned and firmly entrenched, offer comfort to those sidelined with fever, flu or vaccine side effects. But you may be surprised to learn the science supporting these recommendations is speculative at best, harmful at worst and comes with caveats.
The symptoms of the Delta variant appear to differ from traditional COVID symptoms. Here’s what to look out for
A the virus has evolved, it seems the most common symptoms have changed too.