Category: Infectious Disease
Second COVID-19 booster dose recommended for certain individuals
People age 50 and older and certain immunocompromised individuals can now get a second booster dose of an mRNA (Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna) COVID-19 vaccine at least four months after receiving their initial booster dose.
What’s next with face masks?
Keep wearing them in public, wear the best mask available and pay attention to fit.
BA.2 subvariant causing nearly 1 in 4 new COVID cases tested in UW virology lab
A subvariant of omicron responsible for a wave of new COVID-19 cases in parts of Europe and Asia is also gradually spreading in the United States, including in Washington state.
What is the new COVID-19 variant BA.2, and will it cause another wave of infections in the US?
BA.2 is the latest subvariant of omicron, the dominant strain of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19. While the origin of BA.2 is still unclear, it has quickly become the dominant strain in many countries, including India, Denmark and South Africa. It is continuing to spread in Europe, Asia and many parts of the world.
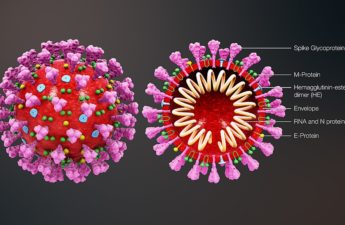
How does the immune system mobilize in response to a COVID-19 infection or a vaccine? 5 essential reads
We sought out scholars who could take our readers on deep dives into immunology and virology to help demystify these sometimes confusing, conflicting and taxing science-based questions. Here are five stories from The Conversation’s archives that highlight critical insights that we as editors and readers have gained thanks to COVID-19, and that will no doubt continue to be an important part of our pandemic lexicon.
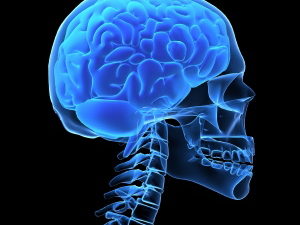
COVID-19 and the brain
Even mild cases of COVID-19 can leave a mark on the brain, such as reductions in gray matter – a neuroscientist explains emerging research.
What King County’s mask mandate rollback means for you
Starting Saturday, March 12, King County will stop requiring masks in many indoor public spaces. Individuals will now be able to make their own choices as to whether they want to continue wearing masks, and businesses may decide whether they want to require employees and customers to wear masks. In practice, what does this mean for you?
No, you cannot ‘devaccinate’ yourself with snake venom kits, bleach or cupping
If you encounter claims like this online, you need to ask yourself four questions, to figure out whether these claims really are too good to be true.
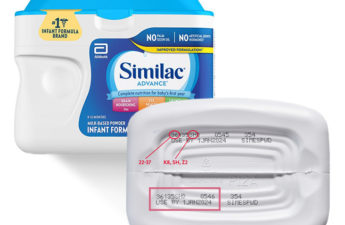
Powdered infant formula recall expands following reports of bacterial infections
Recalled formulas may be linked to several Cronobacter illnesses, two nationwide infant deaths
King County marks two years of COVID outbreak, looks ahead to next phase of pandemic response
King County has gone from the epicenter of the outbreak, to now one of the nation’s highest vaccinated communities with the some of the lowest cases and death rates two years later.
King County’s local indoor mask mandate to end after March 11
Lifting the indoor mask mandate does not mean COVID is over. The use of high quality, well-fitting masks still make sense in certain settings. It is very reasonable to continue to mask if you are at increased risk, are in contact with someone at high risk, out of consideration for people who may be at higher risk in public settings, or if you want to reduce your own risk for any reason.
How long does protective immunity against COVID-19 last after infection or vaccination? Two immunologists explain
Upon vaccination or infection with COVID-19, your body produces two types of protective immune responses. The first type involves B cells, which produce antibodies, the second involves T cells, your second line of defense.
Eight changes the world needs to make to live with COVID
The world pre-2020 no longer exists – we may want it to, but it just doesn’t.
King County’s vaccination verification policy to end March 1st.
King County is ending the local health order requiring proof of COVID-19 vaccination or a negative test for entry into restaurants and bars, indoor recreational events and establishments, or outdoor events.
Lifesaving COVID Medications Can Be Hard to Come By
Early in the pandemic, states competed for the limited supply of ventilators, personal protective equipment and tests in a chaotic free-for-all. To avoid a repeat, the federal government is buying millions of doses of the COVID-19 therapeutic medications and allocating those to states, which in turn distribute them to pharmacies or hospitals. In many places, what is arriving is far less than the need.