Category: Weight Loss
Castor oil is all the rage among health influencers – what you need to know about this alternative remedy
Castor oil, which was once used by fascists in Italy as punishment because of its quick-acting laxative effect, is now a weight-loss trend on TikTok. Not drinking it, but rubbing it on your belly.
Influencers are also pouring it in their belly buttons and wrapping towels soaked in it around their midriff. They claim it can melt belly fat and help with bloating.
Health News Headlines
Measles cases triple – 400 million have had long covid – Pesticides on fruits and vegetables.
Why Millions Are Trying FDA-Authorized Alternatives to Big Pharma’s Weight Loss Drugs
Dry industry officials estimate that several large compounding pharmacies are provisioning up to 2 million American patients with regular doses of semaglutide, the scientific name for Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy, Ozempic, and Rybelsus formulations, or tirzepatide, the active ingredient in Eli Lilly’s Zepbound and Mounjaro.
Stop asking me if I’ve tried keto: Why weight stigma is more than just being mean to fat people
Fat stigma can take the form of overt discrimination, but it is often insidious, pervasively entrenched into our society and environment.
Drugs like Ozempic won’t ‘cure’ obesity but they might make us more fat-phobic
Ironically, while fat people are told they need to lose weight for their health, they are also shamed for “cheating” or taking shortcuts by using medication.
Considering taking a weight-loss drug like Ozempic? Here are some potential risks and benefits
As they’ve grown in popularity, we’ve also heard more about the potential side effects – from common gastrointestinal discomforts, to more serious mental health concerns.
Millions of older people don’t get enough nutrients – how to spot it and what to do about it
Weight loss in older adults is a key sign of malnutrition that needs to be addressed – but it can be easily missed, especially when many older adults associate the idea of thinness with good health. But clothing that’s too loose or a watchstrap that floats on the wrist are all warning signs of undernourishment.
How much weight do you actually need to lose? It might be a lot less than you think
Losing just 5–10% of our body weight – between 6 (~13 lb.)and 12kg (~26 lb.) for someone weighing 120kg (~264 lb.) – can significantly improve our health in four key ways.
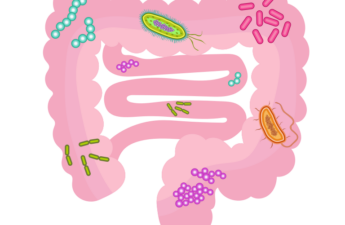
Your body already has a built-in weight loss system that works like Wegovy, Ozempic and Mounjaro – food and your gut microbiome
Specialized bacteria in your lower gut take the components of food you can’t digest like fiber and polyphenols – the elements of plants that are removed in many processed foods – and transforms them into molecules that stimulate hormones to control your appetite and metabolism.
As Zepbound dominates headlines as a new obesity-fighting drug, a nutritionist warns that weight loss shouldn’t be the only goal
Weight loss medications are intended to be used in conjunction with lifestyle changes, such as exercise and a healthy diet. But too often, people view them as a silver bullet for weight loss. And the high price tag and variable insurance coverage for these popular weight loss drugs create a barrier for many people.
Cardio or weights first? A kinesiologist explains how to optimize the order of your exercise routine
When you enter the gym, which way should you head first? Toward the treadmills and spin studio to get your sweat on with a cardio session? Or toward the free weights and strength-training machines to do some resistance training? The answer to this question is … it depends.
Resistance (exercise) is far from futile: The unheralded benefits of weight training
For too long, though, one way of keeping fit, aerobic exercise, has been perceived as superior to the other, resistance training, for promoting health when, in fact, they are equally valuable, and both can get us to the same goal of overall physical fitness.
What does weight-inclusive health care mean?
Weight-inclusive health care means a focus on better health with no weight loss required.
Can I actually target areas to lose fat, like my belly?
Our bodies decide where we store fat and where we lose it from first. And over-the-counter pills and supplements cannot effectively target fat loss either.
What is the OMAD diet? Is one meal a day actually good for weight loss? And is it safe?
Like most weight-loss programs, the OMAD diet makes big and bold promises. Here’s what you need to know about eating one meal a day and what it means for weight loss.