Category: Newborn and Infant Health
Combatting the measles threat means examining the reasons for declining vaccination rates
The anti-vaccine literature is not anti-science. It is filled with statistics and references to scientific studies, although the facts are often wrong. Parents who read this literature need more than the simple reassurance of experts that vaccines are safe and effective. They need to be shown evidence and have confidence that their concerns are being taken seriously.
‘Pandemic babies’ turn 5: Here’s what research tells us about their development and remarkable resilience
Given the effects early-life stress exposure has on a child’s development, many people worried the pandemic would create a generation of children who wouldn’t achieve their potential. But the most recent evidence suggests that pandemic babies are doing better than anyone expected.
Flu kills two area children
The first was an elementary-age child. The second was a preschool-age child.
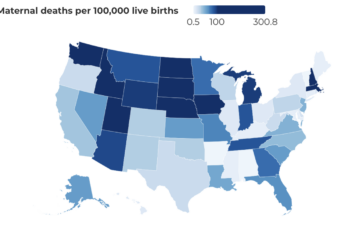
Maternal death reviews get political as state officials intrude
Every state has a committee of medical and public health experts tasked with investigating deaths that occur during and after pregnancy. But as data paints a clearer picture of the impact that state policies such as abortion bans and Medicaid expansion can have on maternal health, leaders in some states are rushing to limit their review committee’s work — or halt it altogether.
Study: Obstetrics Units in Rural Communities Declining
According to the researchers, the decline of obstetrics units in rural communities is contributing to rising maternal morbidity rates.
How mother’s diet affects baby’s health: What insights from different cultures can tell us
A high-quality diet in pregnancy and healthy weight before pregnancy can reduce the risk of gestational diabetes and reduce the chance of transmitting this risk to one’s offspring.
How did polio reemerge in Gaza after a quarter of a century? Q&A with a virologist
We asked a virologist to explain how the virus emerged in the region after all this time, and how it will be dealt with._
Health News Headlines
60% of baby food doesn’t meet nutrition standards – High school football has become a public health crisis – Catching up on sleep at weekends may lower heart disease risk by a fifth
Wildfire smoke is a health risk for pregnant people — both physically and mentally
As the West’s wildfire season worsens, a new Human Rights Watch report urges policymakers to address the toll it’s taking on pregnancy and birth outcomes.
Measles outbreak in Oregon continues to spread
The outbreak of 23 measles cases coincides with spreading cases of whooping cough, which have surpassed 400 this year
Prenatal supplements fall woefully short in providing crucial nutrition during pregnancy – and most women don’t even know it
Prenatal supplements are not the insurance plan that many doctors believe them to be.
SNOHOMISH COUNTY LOSING INFANTS TO UNSAFE SLEEP
From 2020 to 2022, Snohomish County lost 19 infants (babies younger than 12 months) because of unsafe sleep. During that same two-year period, zero infants died due to car crashes, falls, burns or drownings. Most sleep-related deaths are preventable.
Risk of death related to pregnancy and childbirth more than doubled between 1999 and 2019 in the US, UW study finds
Most maternal deaths are considered preventable because, in the U.S., maternal deaths are most often caused by problems that have very effective treatments, including bleeding after delivery, heart disease, high blood pressure, blood clots and infections.
COVID-19 vaccination and boosting during pregnancy benefits pregnant people and newborns
The researchers found that pregnant women who received the COVID-19 vaccines generated antibodies against specific types of SARS-CoV-2. These antibodies crossed the placenta and were also found in the cord blood of vaccinated participants. This likely conferred some protection in the newborns against infection immediately after birth—a critical time when they are vulnerable to severe COVID-19 disease but are too young to be vaccinated.
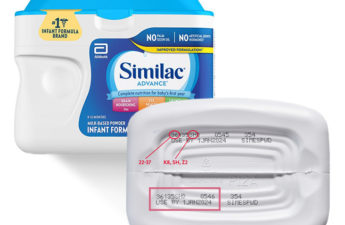
Powdered infant formula recall expands following reports of bacterial infections
Recalled formulas may be linked to several Cronobacter illnesses, two nationwide infant deaths