Doctors who previously never mixed work with politics are jumping into the abortion debate by lobbying state lawmakers, campaigning, forming political action committees and trying to get reproductive rights protected by state law.
Addressing obesity, smoking and workplace ergonomics could cut the burden of low back pain by 39%s
Low back pain has ranked first among causes of disability for the last three decades. Back pain, however, is not inevitable, even if that sometimes feels like the case.
Migraine: A common headache disorder that is underdiagnosed and undertreated
Melina Albanese, University of Toronto Migraine is a common chronic health condition and a leading cause of disability globally. However, even in Canada, with a universal health-care system, migraine is underdiagnosed and undertreated. This is an important public health issue…
Australian study links holiday feasting to yo-yo weight gain
Easter, a time of chocolate eggs and hot cross buns, saw a an average gain of about 244g (0.29% of average participant body weight). The Australian summer months associated with Christmas and New Year, feasts and festivities, had an even larger average increase of approximately 546g (0.65% of average participant body weight). We also found a weekly cycle, with weight peaking on the weekend, when many people are likely letting their hair down after a busy work week and may be drinking and eating more.
What is atrial fibrillation, the heart condition US President Joe Biden lives with?
More than 37.5 million people globally also have atrial fibrillation, but many don’t realise they have it. For most, the condition has few symptoms and does not limit daily life. However, identifying it and treating it is the only way to reduce its serious health consequences.
Good news for ‘weekend warriors’: people who do much of their exercise on a couple of days still get heart benefits
If it is difficult or impossible to find time to be active during a busy week, it is good enough to plan moderate to vigorous physical activities in a couple of weekdays or on the weekend.
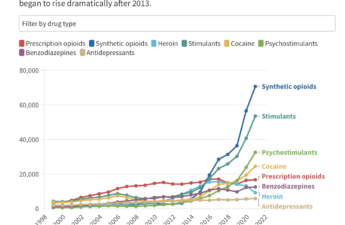
States stiffen penalties for fentanyl, despite public health concerns
Critics argue that harsh penalties could deter those in need of help and worsen societal disparities.
Women treated for breast cancer may age faster than cancer-free women
Among women diagnosed with breast cancer, the association with faster biological aging was most pronounced for those who received radiation therapy, while surgery showed no association with biological aging.
FDA approves first daily over-the-counter birth control pill, Opill – a pharmacist and public health expert explain this new era in contraception
The FDA’s approval of the first-ever over-the-counter daily birth control pill means that people could soon get them from the same aisles as aspirin, eye drops or condoms.
How to Prepare for an Early and Long 2023 Wildfire Season in King County
his year, wildfire smoke is forecast to start early in King County and last into the fall. Record-setting forest fires have already darkened skies in Canada and the eastern U.S., and our region is set to be next. By preparing now, you can help to protect your and your family’s lungs, heart, and health from smoke.
Stay Ahead of the Class: Ways to Get Your Family Caught Up on Vaccinations Before the New School Year Starts
Now’s the perfect time to make sure your child has the vaccinations they’ll need to start the new year without a hitch. Not only are vaccines required for school and childcare, they’re also one of the best tools you’ve got to help your child stay healthy and thrive, this year and beyond.
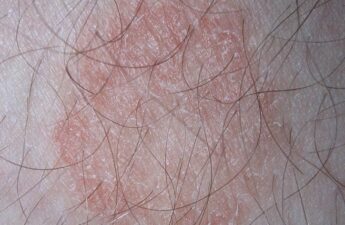
Ringworm fungal infections are common in the US and are becoming increasingly resistant to treatment – 6 questions answered
Ringworm infection is a common infection of the skin caused by a fungus. It’s estimated that at any given time about 20%-25% of Americans will have an active ringworm infection.
Aspartame: popular sweetener could be classified as a possible carcinogen by WHO – but there’s no cause for panic
So far, the regulators have all agreed that it’s safe for a person to consume 40mg of aspartame per kilogram of their body weight per day. That’s about 2.8g for a 70kg adult – and is much more than most people consume.
Fiber is your body’s natural guide to weight management, say UW expert
Rather than cutting carbs out of your diet, eat them in their original fiber packaging instead
Intermittent fasting and calorie counting about equal for weight loss – new study
Is intermittent fasting any better than calorie counting for losing weight? A new study, published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, aimed to provide the answer. It showed that the two methods could be equally effective – if undertaken with professional counselling.