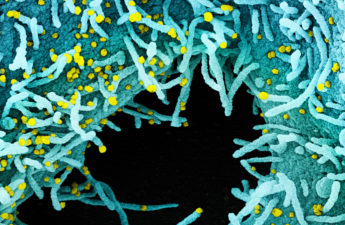
There remains some debate among public health experts about whether the pandemic is “over” — or whether it realistically can ever be. There is no official arbiter for making that decision, and the word “over” suggests a finality that is not well suited for describing a pathogen that will exist in some form indefinitely. However, we found broad agreement among infectious-disease specialists that the pandemic by now is “under control.”
Most States Are Wary of Mandating COVID Shots for Kids
Many parents who have not gotten their children vaccinated say the absence of full FDA authorization is a factor, since it suggests that the vaccines have not been fully vetted.
What’s this ‘longevity’ diet, and will it really make you live longer?
Foods in this diet are vegetables, including leafy greens, fruit, nuts, beans, olive oil, and seafood that’s low in mercury.
COVID-19 vaccine clinics come to state colleges
While the focus of these clinics will be providing the recently released Omicron-targeted bivalent boosters, primary series vaccines from both Pfizer BioNTech and Moderna will also be available.
Pace as important as 10,000 steps for health, studies find
“The take-home message here is that for protective health benefits people could not only ideally aim for 10,000 steps a day but also aim to walk faster.”
75 Hard: what you need to know before taking on this viral fitness challenge
Although the requirements of the 75 Hard challenge are pretty outlandish by most people’s standards, seeing the transformations and online testimonials of how the challenge changed lives may explain why many continue to be curious about it.
When does COVID become long COVID?
And what’s happening in the body when symptoms persist? Here’s what we’ve learnt so far
When abortion at a clinic is not available, 1 in 3 pregnant people say they will do something on their own to end the pregnancy
Overall, 34% of pregnant women surveyed would definitely or probably consider doing something on their own to end their pregnancy if they couldn’t get an abortion in a clinic.
Inslee: Washington’s COVID-19 emergency to end Oct. 31
Nearly three-quarters of Inslee’s 85 emergency orders related to the virus have already been lifted, and an additional 13 health care related orders will end on Oct. 27. The remaining 10 orders, including the underlying state of emergency, will be lifted on Oct. 31.
Fears of a polio resurgence in the US have health officials on high alert
A virologist explains the history of this dreaded disease
Using nanotechnology and AI to diagnose TB in children
Combining nanotechnology with artificial intelligence can diagnose tuberculosis in children in whom the deadly disease might otherwise go undetected.
Omicron COVID-19 vaccine boosters now authorized for certain individuals
New boosters aim to provide better protection from currently-circulating variants of COVID-19
Some Abortion Bans Put Patients, Doctors at Risk in Emergencies
Ever since the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade, emergency health care providers in states that ban abortion have had to make wrenching legal and ethical judgments before treating a pregnant woman whose health or life may be in peril.
Methamphetamine Use, Overdose Deaths, and Arrests Soared From 2015 to 2019
From 2015 to 2019, arrests for meth possession increased 59%; the number of people in the U.S. with a methamphetamine-related substance use disorder jumped 37% and overdose deaths involving meth more than doubled.
When can I get the updated covid booster — Public Health – Seattle & King County
The very earliest we could expect to have the new booster doses available at our vaccination sites at the Auburn Outlet Collection Mall would be the weekend of September 9th. However, delays in shipping are possible, so it could be later.