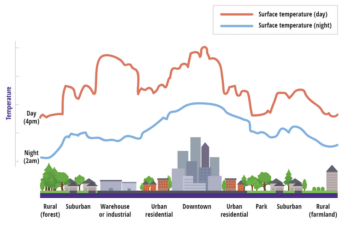
Promoting healthy lifestyles, early disease detection and timely treatment could reduce chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease and cancer. And reducing the number of people with these chronic conditions would lead to a significant decrease in healthcare spending – which has been steadily rising in real terms.
Vaccination in pregnancy greatly reduces risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19, and protects babies up to 6 months after birth
Extensive evidence shows COVID-19 vaccinations in pregnancy are safe, when given at any time during the pregnancy.
Dementia linked to repetitive brain trauma diagnosed in a female athlete for first time
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a devastating form of dementia which causes a decline in brain functioning and increased risk of mental illness. It is increasingly associated with athletes who play contact sports, such as football, boxing and martial arts.
Do psychedelics really work to treat depression and PTSD? Here’s what the evidence says
Early results from studies around the world have found psychedelic therapy might be effective for treating a range of psychological issues. However, as psychedelic research has grown, limitations of the research have been identified by researchers both within and outside the psychedelic field. One issue is that we aren’t sure whether findings might be due to a placebo effect, which occurs when a treatment works because people expect it to work.
BMI alone will no longer be treated as the go-to measure for weight management – an UW obesity expert explains
Ultimately, BMI cannot provide doctors with precise information about the portion of body weight composed of body fat, nor can it tell us how that fat is distributed in the body. But this distribution is important because research has shown that fat stored around the internal organs has significantly higher health risks than that distributed in the extremities
Acetaminophen vs ibuprofen — which works best and when?
Deciding which one you should choose is dependent on the type of pain you are experiencing. Sometimes it might be appropriate to take a medication that contains both drugs.
Saving lives from extreme heat: Lessons from the deadly 2021 Pacific Northwest heat wave
The 2021 heat dome was Washington’s deadliest weather disaster on record. It contributed to 441 deaths in the state between June 27 and July 3, our research shows. Medical systems were overwhelmed. There are numerous ways to avoid this deadly of an outcome in the future. Many emerge from thinking about extreme heat as long-term risk reduction, not just short-term emergency response.
Snooping in Medical Records by Yakima Valley Memorial Hospital Security Guards Leads to $240,000 HIPAA Settlement
The information accessed included names, dates of birth, medical record numbers, addresses, certain notes related to treatment, and insurance information.
Big hair? Bald? How much difference your hair really makes to keep you cool or warm
When humans moved from living in the jungle to the savannah, they needed to walk and run long distances in the sun. This meant they needed a way to handle the increased body temperature that comes with physical activity in the heat.
Sweating is the best way to lose heat and cool down, but the presence of hair reduces sweating and heat loss from the skin. So humans evolved to lose body hair to be better adapted to exercising in the heat. Fewer hair follicles in our skin made room for more sweat glands. This made our skin optimal for sweat evaporation – and the heat loss that goes with it – to keep us cool.
Wildfire smoke forecasted to impact Washington again this season
‘Smoke Ready Week,’ June 12-16, is the perfect time to prepare for unhealthy air
Mpox update from Public Health — Seattle & King County:
WHY A SECOND VACCINATION IS IMPORTANT NOW
How the Mixed Messaging of Vaccine Skeptics Sows Seeds of Doubt
By Darius TahirKaiser Health News It was a late-spring House of Representatives hearing, where members of Congress and attendees hoped to learn lessons from the pandemic. Witness Marty Makary made a plea. “I want to thank you for your attempts…
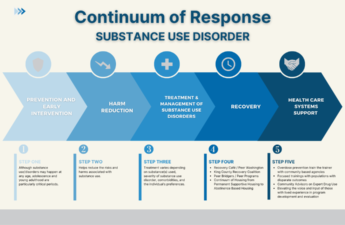
Local resources for those with drug use disorders
Treatment: What’s available and how to access it
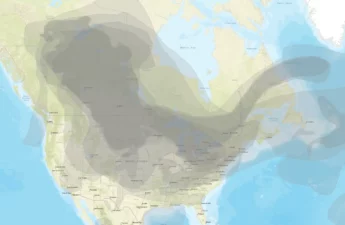
Climate Crisis Is on Track to Push One-Third of Humanity Out of Its Most Livable Environment
Climate change is remapping where humans can exist on the planet. As optimum conditions shift away from the equator and toward the poles, more than 600 million people have already been stranded outside of a crucial environmental niche that scientists say best supports life. By late this century 3 to 6 billion people, or between a third and a half of humanity, could be trapped outside of that zone, facing extreme heat, food scarcity and higher death rates, unless emissions are sharply curtailed or mass migration is accommodated.
How wildfire smoke can harm human health, even when the fire is hundreds of miles away – a toxicologist explains
One concern is that smoke can suppress macrophage function in the lung, altering the immune cell’s function enough that you become more susceptible to respiratory infection.