In Washington, a new team of epidemiologists is preparing for a hotter, smokier future.
Balance declines with age, but exercise can help stave off some of the risk of falling
A number of physical changes with aging often go unseen preceding falls, including muscle weakness, decreased balance and changes in vision.
Am I too old to build muscle?
What science says about sarcopenia and building strength later in life
Rural Health Clinics with ‘Head-to-Toe and Womb-to-Tomb’ Care
Rural health clinics are safety net providers whose original mandate was primarily to increase access to care for those on Medicaid or Medicare. They provided primary care and perhaps a few other services. But the Rural Health Clinic program has evolved over the years, and some clinics, like Primary Care Centers of Eastern Kentucky, have expanded their roles quite considerably.
Health disparities cost to U.S. economy tops $450 billion a year
Most of the economic burden for racial and ethnic disparities was borne by Black/African American population (69%) due to the level of premature mortality. Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander ($23,225) and American Indian/Alaska Native ($12,351) populations had the highest economic burden per person.
Study Reveals Staggering Toll of Being Black in America: 1.6M Excess Deaths Over 22 Years
Because so many Black people die young — with many years of life ahead of them — their higher mortality rate from 1999 to 2020 resulted in a cumulative loss of more than 80 million years of life compared with the white population, the study showed.
One in five US adults report persistent, chronic pain, study finds
Overall, the study found that the rate of chronic pain and high-impact chronic pain among adults is approximately 21% and 8%, respectively. Chronic pain is pain that is experienced on most days or every day in the past three months; and high-impact chronic pain s pain that limits life or work activities on most days or every day during the past three months.
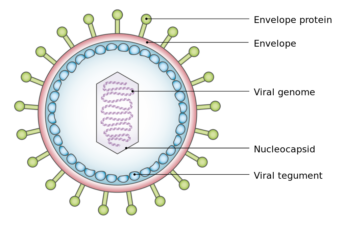
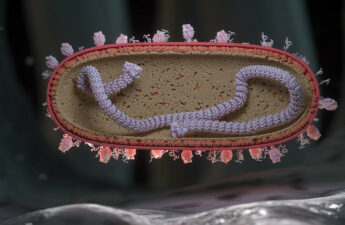
Going long: Viruses linger with lasting impact
Herpes, HIV, Epstein-Barr and other viruses hang around, causing potential long-term health woes. Should ‘long COVID’ surprise us?
‘Grotesque Catch-22’ – Sickest Rural Adults Are the Least Likely to Be Able to Pay for Healthcare
Research on cost barriers to health care found that rural adults were more likely than urban adults to report being unable to pay their medical bills or have problems paying their medical bills. Rural adults also were more likely to use medications in ways not prescribed (like taking pills every other day or only filling prescriptions every other month) to save money on medication.
Heat Advisory Issued this Weekend for Washington State
The National Weather Service is forecasting temperatures in the high 80s and low 90s for much of western Washington by Monday. Since many Washingtonians do not have air conditioning in their homes, cooling off can be a challenge, particularly for people with health conditions, the elderly, and infants.
Obesity in children is rising dramatically, and it comes with major – and sometimes lifelong – health consequences
Without intervention, many obese adolescents will remain obese as adults. Even before adulthood, some children will have serious health problems beginning in their preteen years.
FDA’s approval of the world’s first vaccine against RSV will offer a new tool in an old fight – 4 questions answered
The new vaccine has been shown to be 80% effective at protecting against RSV-related disease and 94% effective at protecting against severe disease.
The Federal COVID-19 public health emergency declaration ends May 11. What does that mean for you?
This Thursday, the Federal Public Health Emergency Declaration will end, which means there will be changes to how some people receive COVID-19-related care, like testing, treatment, and vaccines.
Ask a Chatbot: ‘What’s for Dinner?’
Some health and wellness professionals say ChatGPT’s ability to have conversations can be useful for generating meal plans and ideas for people who have specific health goals and dietary needs.
Risk of rehospitalization in younger women after heart attack nearly double that of men
Higher rates of risk factors such as obesity, heart failure, and depression among women most likely contributed to the disparity.